What is 3D Printing in Automotive Industry?
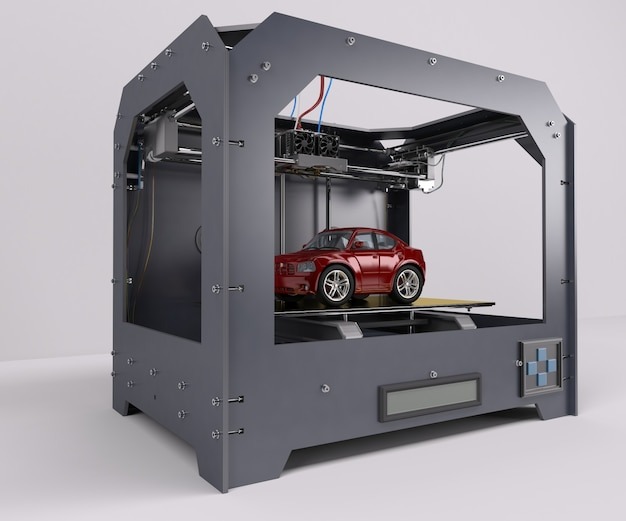
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has become a transformative force in several industries, including automotive. This advanced manufacturing technique involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital file. Its ability to fabricate complex designs with precision and minimal waste makes it a game-changer in automotive engineering.
In the automotive sector, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, lightweight part production, and even end-use parts. From creating bespoke tools to manufacturing electric vehicle parts, the list goes on. Let’s take a closer look at the relevance, uses, and the best 3D printers for automotive parts.
How 3D Printing Works in Automotive Manufacturing
The 3D printing process begins with a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model. After the digital blueprint is made:
1. Design Preparation: The design is sliced to layers using slicing software.
2. Material Loading: Thermoplastic or metal powder material loaded in the printer
3. Printing: Materials are deposited layer by layer into the part by using technologies such as FDM, SLS.
4. Post-processing: the printed part is cleaned and polished or treated for its final finish.
Applications of 3D Printing in Automotive Industry
3D printing’s versatility has enabled its adoption across various automotive domains:
1. Rapid Prototyping
Engineers can quickly create prototypes to test designs and functionality, significantly shortening the development cycle.
2. Tooling and Fixtures
Manufacturers produce custom jigs, fixtures, and tools with precision, enhancing production efficiency and reducing costs.
3. Production of Lightweight Parts
3D-printed parts, like brackets or engine components, use less material while retaining structural integrity, reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency.
4. On Demand Spare Parts
Automobile manufacturers can manufacture spare parts in-house without having to inventory them; this way, they do not incur stock costs, and customers obtain what they want faster.
5. Personalization
Options for personalization are there, including unique, tailor-made components, for specific niches and high-performance car consumers.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Automotive Industry
• Cheap: Avoids waste material and is free from high-cost tooling.
• Time-Effective: Provides quick-to-market designs as well as quick-to-assemble product.
• Flexibility: Allows for the creation of complex designs that are not possible with traditional methods.
• Sustainability: Reduces material usage and promotes green practices.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Automotive
Despite its benefits, 3D printing presents some challenges:
• Material Limitations: Few choices for high-temperature or high-stress applications.
• Initial Costs: Heavy investment in advanced 3D printers and training.
• Scalability: Mass production using 3D printing is still a challenge.
Things to Consider Before Selecting a 3D Printer
Consider the following when choosing a 3D printer for automotive parts:
• Material Compatibility: Ensure that the printer supports materials suited for your application.
• Build Volume: Larger printers are ideal for producing bigger components.
• Precision and Resolution: It is critical in creating complex parts.
• Cost and Maintenance: Affordability must be balanced with functionality.
The Future of 3D Printing in Automotive
3D printing in automotive manufacturing is still growing, promising further developments such as:
• Electric Vehicles (EVs): Lightweight and efficient components for EVs.
• AI Integration: Smarter Printers that optimize designs for best performance
• Sustainable Practices: Greater use of recyclable material
Conclusion
3D printing is changing the automotive industry through innovation, efficiency, and customization. With its continued evolution, the use of 3D printing in automotive design and manufacturing will continue to grow, allowing for a more sustainable and advanced industry. The right 3D printer will open doors for automakers in unprecedented possibilities, from rapid prototyping to high-quality end-use parts.